- Home
-
Academic Outputs
-
PRIME Academic Outputs
-
-
Evidence Map
-
PRIME Evidence Map
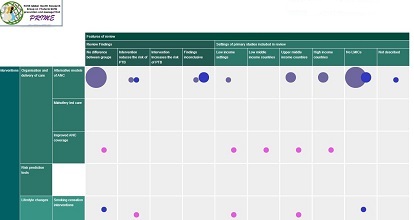
The PRIME Evidence Map is an interactive table that summarises the evidence from 137 published systematic reviews published in the past decade. Each included systematic review has examined the effectiveness of an intervention to reduce the risk of preterm birth. This includes a range of both primary and secondary interventions.
The map demonstrates a number of the study features. This includes the overall result for the effect of the intervention on risk of preterm birth. The number of included participants and also the study location were noted and categorised (low income, low middle income, upper middle income and high income countries) for each included primary study.
The size of the dot indicates the number of reviews (more reviews – the larger the dot). The colour of the dot gives an indication of the number of primary studies in those reviews (the code is at the bottom of the page). If you click on a dot it takes you to the reference and abstract. The map can be both a resource for locating evidence and also highlighting where gaps exist. This is a resource that will be updated and if you feel there is a recent systematic review that should be included please email me and it can be added.
I hope you find it useful!
Fiona Campbell.
-
- About
- Events
-
News & Blogs
- Contact